In today’s digital landscape, ensuring that your organization’s policies are accessible on your website isn’t just good practice—it’s essential for Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) and The Campaign Registry (TCR) compliance. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies around business text messaging practices, companies must demonstrate transparency through clear, readily available documentation of their consent and privacy policies. The intersection of website accessibility and messaging compliance represents a critical area where businesses can either build trust with consumers or expose themselves to significant regulatory and reputational risk.
The Growing Importance of Policy Accessibility in Digital Communication
The evolution of business messaging has accelerated dramatically over the past several years. What began as a novel marketing channel has become an essential component of customer engagement strategies across virtually every industry. With this growth has come increased attention from regulators, consumer advocacy groups, and privacy-conscious customers who demand transparency about how their personal information is collected, used, and protected.
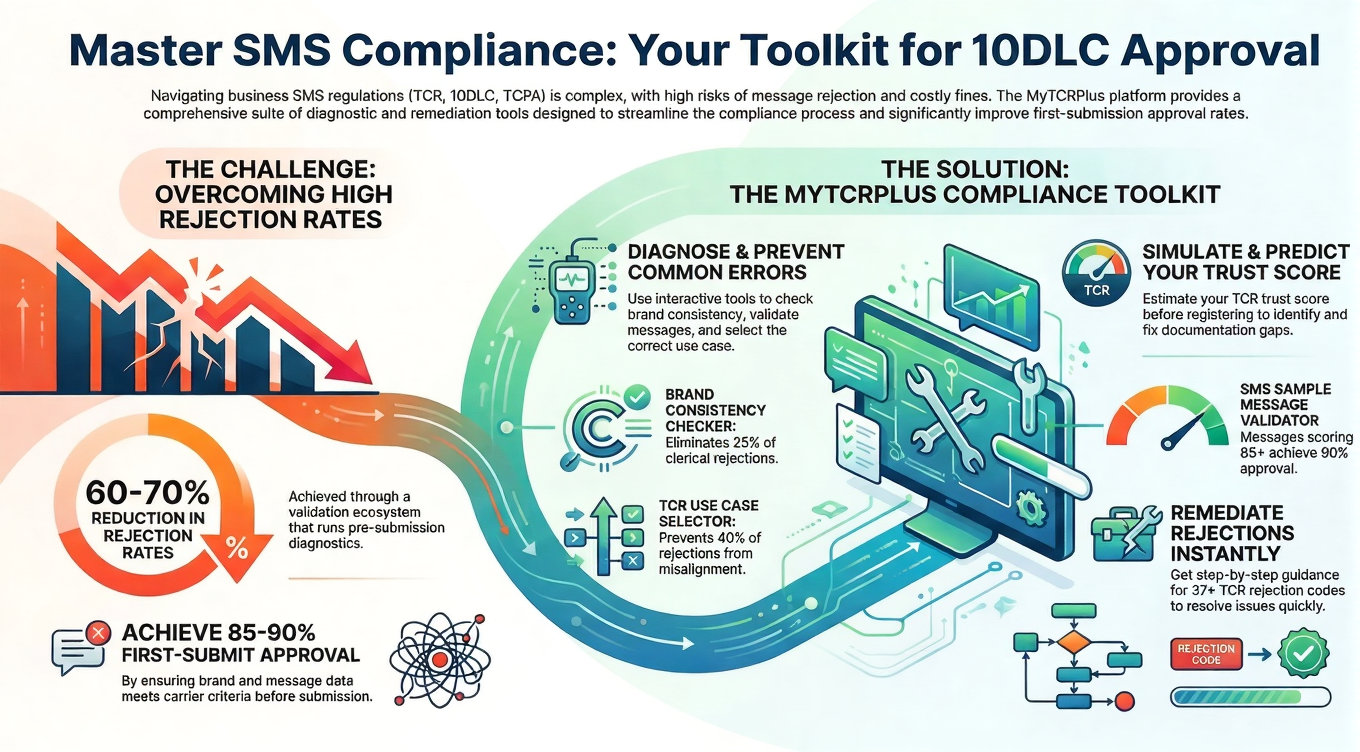
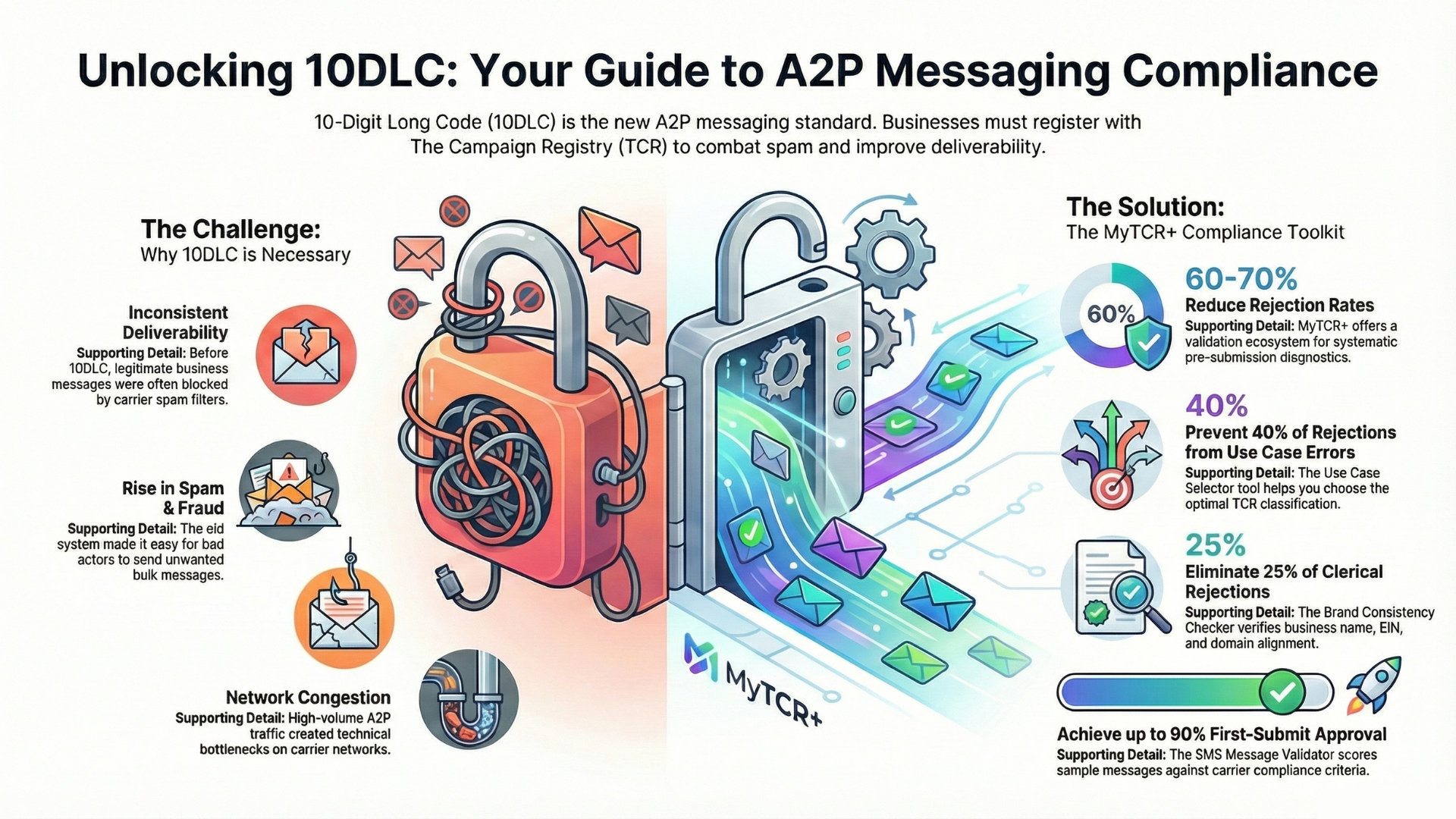
The TCR framework requires businesses engaged in Application-to-Person (A2P) messaging to register their campaigns and provide evidence of proper consent mechanisms. This registration system was implemented to combat spam, protect consumers, and create accountability in the SMS messaging ecosystem. Central to this compliance framework is making certain policies publicly accessible on your website, creating a transparent record that regulators, carriers, and consumers can reference to verify your organization’s commitment to lawful messaging practices.
These documents serve as proof that your organization follows lawful practices when collecting phone numbers and obtaining permission to send marketing messages. They’re not merely formalities or box-checking exercises—they represent your public commitment to ethical communication practices. When disputes arise or regulators investigate complaints, the first place they’ll look is your website to understand your stated policies and determine whether your actual practices align with your public commitments.
Essential Policy Documents for TCR Compliance
At the heart of TCR compliance lies your privacy policy and terms of service, two foundational documents that govern the relationship between your business and its customers. These documents must clearly articulate how your company collects, uses, stores, and protects consumer data, particularly phone numbers used for text messaging campaigns. The specificity and clarity of these policies directly impact both your compliance status and your ability to defend your practices if challenged.
Your privacy policy should explicitly address SMS communications in dedicated sections rather than treating messaging as an afterthought buried within general data collection language. This section should explain what types of messages consumers can expect to receive, whether they’ll primarily receive promotional offers, transactional updates, account notifications, or a combination of message types. Setting accurate expectations prevents consumer surprise and reduces complaint rates significantly.
Frequency disclosure is another critical element that must be clearly communicated. Consumers need to understand whether they’ll receive daily messages, weekly updates, or occasional communications. If message frequency varies by campaign or season, this variability should be explained. Hidden or unclear frequency disclosures often become the basis for consumer complaints and regulatory scrutiny, as customers feel deceived or overwhelmed by messaging volume they didn’t anticipate.
The opt-out process deserves prominent, unambiguous explanation in your policies. Consumers must know that they can discontinue receiving messages at any time and understand the simple mechanism for doing so. Standard language like “Reply STOP to unsubscribe” should be clearly documented, along with any alternative opt-out methods you provide. The policy should also explain what consumers can expect after opting out, including confirmation that their request was processed and the timeframe within which messages will cease.
Beyond privacy policies, your terms of service should address the contractual aspects of your messaging program. This includes any costs consumers might incur, such as message and data rates from their carriers, disclaimers about message delivery reliability, and any limitations on your liability for delayed or failed message delivery. While consumers bear responsibility for their own carrier charges, transparent disclosure of this reality demonstrates good faith and prevents misunderstandings.
SMS-specific terms and conditions create another layer of documentation that sophisticated messaging programs should maintain. These focused documents can provide detailed information about individual messaging campaigns, specific opt-in processes, and program-specific rules that might differ from your general privacy policy. For businesses running multiple messaging campaigns with different characteristics, program-specific documentation helps avoid confusion and provides clarity for each distinct use case.
Strategic Placement and Navigation: Making Policies Truly Accessible
Accessibility goes beyond merely having these policies exist somewhere on your website. They must be genuinely easy to find and navigate, meeting both regulatory requirements and user experience best practices. A policy that technically exists but can only be found through dedicated searching or multiple navigation steps fails the fundamental accessibility test.
Best practices suggest placing links to your privacy policy, terms of service, and any SMS-specific policies in your website footer, where users universally expect to find them. This convention has been established across the internet over decades, creating user expectations that businesses violate at their peril. Footer placement ensures visibility without cluttering primary navigation or interfering with conversion-focused page elements.
These links should be present on every page of your site, ensuring that regardless of where a visitor enters or browses, they can quickly locate your policies. Inconsistent policy links that appear on some pages but not others create confusion and suggest organizational sloppiness that may extend to compliance practices more broadly. Universal accessibility also matters for direct linking—when sharing your privacy policy with regulators, partners, or concerned consumers, consistent URLs that work from any context simplify reference and verification.
Consider implementing multiple pathways to your policy documents. Beyond footer links, relevant policies should be linked directly within opt-in forms, on account creation pages, during checkout processes, and anywhere else consumers provide personal information or consent to communications. Contextual policy links at the point of data collection demonstrate transparency and give consumers immediate opportunity to review terms before committing.
Internal search functionality represents another accessibility mechanism worth optimizing. Consumers who search for “privacy policy,” “SMS terms,” “text messaging,” or related queries should immediately find relevant policy documents. Regular testing of search functionality from a user perspective helps identify gaps where policy documents might be underperforming in search results despite their importance.
Your website’s main navigation might also warrant inclusion of policy links, particularly for businesses where data privacy and transparent communication practices serve as competitive differentiators. While not universal practice, some organizations prominently feature their commitment to privacy and transparency by elevating policy access beyond standard footer placement.
Writing Policies That Humans Can Actually Understand
The language within these policies matters tremendously, yet remains one of the most commonly overlooked aspects of policy development. While legal precision is necessary to ensure policies provide adequate protection and satisfy regulatory requirements, readability shouldn’t be sacrificed in pursuit of legal comprehensiveness. Consumers need to understand what they’re agreeing to when they provide their phone number, and impenetrable legal jargon defeats the purpose of public disclosure.
Using clear, jargon-free language demonstrates respect for your audience and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings that could lead to complaints or regulatory issues. Consider having policies reviewed not just by legal counsel but also by marketing professionals, customer service representatives, and even sample consumers who can provide feedback on comprehension. If your frontline customer service team struggles to explain your policies, there’s strong indication that consumers will similarly struggle to understand them.
Organizational structure significantly impacts readability. Breaking policies into logical sections with descriptive headings allows readers to quickly navigate to relevant information rather than wading through entire documents. A table of contents for longer policies provides additional navigation assistance. Bullet points and numbered lists make complex information more digestible than dense paragraphs of continuous text.
Plain language doesn’t mean oversimplification that sacrifices accuracy or legal sufficiency. Rather, it means expressing necessary concepts in the clearest possible terms. For example, instead of “We may utilize your telephonic contact information for the dissemination of promotional communications,” consider “We may use your phone number to send you marketing messages about our products and special offers.” Both versions convey the same information, but one respects the reader’s time and cognitive load.
Consider providing layered disclosures where appropriate. A short, plain-language summary of key points can appear at the beginning of policy documents, followed by more detailed legal language for those who want or need comprehensive information. This approach serves both the consumer seeking quick understanding and the compliance officer or attorney conducting detailed policy review.
Definitions sections clarify technical or legal terms that must be used within policies. Rather than assuming consumers understand terms like “A2P messaging,” “SMS,” “opt-in consent,” or “personal identifiable information,” provide clear definitions that establish shared understanding. This is particularly important given the technical nature of messaging compliance.
Mobile Optimization: Meeting Users Where They Are
Mobile accessibility deserves special attention since many users will access your policies from their smartphones. This isn’t merely a convenience issue—it’s about ensuring that the very audience you’re seeking to reach via text messaging can actually review your policies on their preferred device. The irony of sending SMS messages to consumers who cannot easily read your SMS policies on mobile devices shouldn’t be lost on compliance-conscious organizations.
Your policy pages must render correctly on smaller screens, with readable font sizes that don’t require zooming or horizontal scrolling. Text size below 14-16 pixels often becomes difficult to read on mobile screens, particularly for users with visual impairments or those viewing policies in less-than-ideal lighting conditions. Responsive design that adapts layout based on screen size ensures policies remain accessible across the full spectrum of devices consumers use.
Proper formatting for mobile includes appropriate line length, sufficient spacing between lines and paragraphs, and touch-friendly interactive elements. Links and buttons should be large enough to tap accurately without accidentally triggering adjacent elements. Expandable sections or accordions can help manage long policy documents on mobile screens by allowing users to reveal only the sections they want to read, reducing overwhelming wall-of-text experiences.
Page load speed matters significantly for mobile policy access, particularly for users on cellular connections rather than WiFi. Heavy policy pages that load slowly create frustration and abandonment. Optimizing images, minimizing unnecessary scripts, and leveraging browser caching can ensure policy pages load quickly even under less-than-ideal connection conditions.
Testing policy accessibility on actual mobile devices across various operating systems, screen sizes, and browsers helps identify real-world usability issues that might not appear in desktop testing. Having team members from different roles—not just developers—review policy pages on their personal devices provides valuable perspective on authentic user experience.
Consider that many consumers will access your policies directly from their phones after receiving a text message that raises questions or concerns. The ability to click a link in your message footer and immediately review relevant policies on mobile device creates a seamless path to transparency that builds trust and reduces complaint escalation.
Maintaining Current, Accurate, and Living Policy Documents
Regular audits of your policy pages are crucial in the dynamic regulatory environment governing business communications. As your messaging practices evolve, your customer base expands, new campaigns launch, or regulations change, your documentation must keep pace with these developments. Outdated or inaccurate policies can create compliance gaps that expose your organization to risk while undermining consumer trust when customers discover discrepancies between stated policies and actual practices.
Implement a review schedule to ensure your policies reflect current practices and regulatory requirements. Quarterly reviews represent a reasonable cadence for most organizations, though companies in highly regulated industries or those experiencing rapid growth might benefit from more frequent evaluation. Each review should assess whether policy language accurately describes current data collection practices, consent mechanisms reflect actual opt-in processes, message type descriptions match campaigns being executed, opt-out procedures document available unsubscribe methods, and frequency disclosures align with actual sending patterns.
Version control and change documentation provide important compliance evidence. When policies are updated, maintaining records of what changed, when changes took effect, and the rationale behind modifications creates an audit trail that demonstrates thoughtful compliance management. Some organizations publish policy change logs or archives of previous versions, though this level of transparency isn’t universally required.
Communication about policy changes deserves careful consideration. When material changes occur—particularly those that affect consumer rights, data usage, or messaging practices—notifying affected users demonstrates good faith and often satisfies regulatory expectations. The method and timing of notification should be appropriate to the significance of changes, with substantial modifications warranting direct communication rather than relying on consumers to notice updated website policies.
Creating Auditable Consent Documentation and Mechanisms
Documentation extends beyond the policies themselves to encompass the systems and processes through which you obtain and record consumer consent. Maintaining records of when and how consumers consented to receive messages is equally important to having well-crafted policies. Your website should include clear opt-in mechanisms, whether through forms, checkboxes, or other interfaces, that create an auditable trail of consent that can withstand regulatory scrutiny.
Consent forms should include several key elements that establish clear, informed agreement. The consumer’s phone number should be explicitly collected in a dedicated field, not buried within other contact information. A clear description of what they’re consenting to should appear adjacent to the consent mechanism, explaining message types, frequency, and opt-out procedures. An affirmative action like checking a box or clicking a button should be required, with pre-checked boxes failing to meet consent standards in most jurisdictions.
The language of consent requests matters significantly. Phrases like “By checking this box, you agree to receive marketing text messages from [Company Name] at the phone number provided” clearly establish what the consumer is consenting to and meet the standard for “prior express written consent” under TCPA requirements. Vague language like “Keep me updated” fails to establish clear consent to specific communication methods.
Recording consent comprehensively creates the documentation needed to defend your practices. Each consent record should capture the phone number provided, the date and time consent was obtained, the IP address or other technical identifiers, the specific consent language presented, the campaign or message type consented to, and the method by which consent was obtained. This granular documentation enables you to demonstrate compliance on a per-number basis if disputes arise.
Integration between your website forms and your messaging platform ensures that consent records flow seamlessly from collection to application. Manual processes or disconnected systems create opportunities for errors, delays, and compliance failures. Automated consent workflows that immediately update messaging lists and document consent reduce risk while improving operational efficiency.
The Broader Benefits of Policy Accessibility and Transparency
The investment in making policies accessible and compliant pays dividends in multiple ways that extend far beyond satisfying TCR requirements. Transparent communication builds consumer trust, which has become an increasingly valuable asset in privacy-conscious markets. When customers understand and feel respected by your messaging practices, they’re more likely to remain engaged, make repeat purchases, recommend your business, and provide positive reviews rather than filing complaints or reporting your messages as spam.
Reduced complaint rates directly impact deliverability and sender reputation. Wireless carriers and messaging platforms monitor complaint rates as key signals of sender quality. Organizations with low complaint rates enjoy better message delivery, faster throughput, and less risk of filtering or blocking. Conversely, high complaint rates can lead to campaign suspension, additional scrutiny, and delivery challenges that undermine messaging effectiveness. Clear policies that set appropriate expectations contribute significantly to maintaining low complaint rates.
Operational efficiency improves when policies are clear and accessible. Customer service teams field fewer questions about messaging practices when policies answer common concerns proactively. Marketing teams can execute campaigns with confidence knowing that proper documentation supports their activities. Compliance teams can more easily demonstrate adherence to requirements during audits or investigations. Legal teams face fewer disputes when policies establish clear terms and obtain informed consent.
Competitive differentiation emerges from transparency in crowded markets where consumers are increasingly sophisticated about privacy. Organizations that clearly communicate their practices and demonstrate respect for consumer preferences can position these commitments as brand differentiators. Privacy-conscious consumers actively seek businesses that take these issues seriously, creating opportunities to attract and retain valuable customer segments.
Future-Proofing Your Compliance Through Accessible Policies
In the evolving regulatory environment surrounding business messaging, proactive accessibility isn’t optional—it’s the foundation of sustainable, compliant text messaging programs. As regulations continue to develop, enforcement intensifies, and consumer expectations rise, the organizations best positioned for success will be those that have built their communication programs on transparent, well-documented foundations.
Looking ahead, several trends suggest that policy accessibility will become even more critical. Regulatory coordination across jurisdictions may create more uniform standards that emphasize transparency and consumer access to information. Technology advances may enable more sophisticated consent verification that relies on documented policies. Consumer advocacy may drive demand for plain-language policies that truly inform rather than obscure. Legal precedents may establish higher standards for what constitutes adequate disclosure and accessible policy documentation.
By investing now in comprehensive, accessible, clearly written policy documentation, organizations not only achieve current compliance but also build resilience for future regulatory developments. The effort required to create excellent policy documentation and accessibility is significant but finite, while the ongoing benefits compound over time through reduced risk, improved consumer relationships, and operational confidence that your messaging programs rest on solid compliance foundations.