![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-1[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-11-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-2[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-21-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-3[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-31-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-4[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-41-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-5[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-51-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-6[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-61-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-7[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-71-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-8[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-81-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-9[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-91-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-10[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-101-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-11[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-111-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-12[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-121-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-13[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-131-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-14[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-141-768x429.png)
![Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-15[1]](https://mytcrplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Short_Code_to_10DLC_Migration_Strategic_Guide_for_E-Commerce_Retailers__slide_deck_-_no_wm-151-768x429.png)
The landscape of business messaging in e-commerce has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, driven by evolving carrier regulations, shifting consumer expectations, and the industry’s need for more transparent and trustworthy communication practices. For many e-commerce platforms—from small independent retailers to large multinational corporations—this has meant transitioning from traditional short code messaging systems to the newer 10DLC (10-Digit Long Code) framework. This migration carries important implications for how businesses connect with their customers, manage compliance, optimize costs, and maintain the messaging deliverability crucial to modern e-commerce operations.
Understanding the Short Code Era: Benefits and Limitations
To appreciate the significance of the shift to 10DLC, it’s essential to understand what short codes represented in the evolution of business messaging and why they became the industry standard for high-volume SMS campaigns. Short codes are five or six-digit numbers that businesses lease from carriers or aggregators to send large quantities of messages to customers. During the height of the short code era, these codes became synonymous with legitimate business communication, used by everyone from retail giants sending flash sale notifications to financial institutions delivering account alerts.
Short codes offered several compelling advantages that made them the preferred solution for major retailers and e-commerce platforms. The most significant advantage was their impressive throughput capability. Well-provisioned short codes could send thousands of messages per second, enabling retailers to communicate with massive audiences virtually simultaneously. During critical business moments—flash sales, limited-time promotions, seasonal events—this capability was invaluable. A major retailer could notify millions of customers about a limited inventory event within minutes, ensuring broad reach before stock ran out.
From a technical perspective, short codes provided reliable message delivery and strong sender reputation. Major carriers prioritized short code messages in their filtering systems, recognizing them as legitimate business communications. This meant that messages sent via short codes had higher deliverability rates compared to other messaging solutions. Customers developed familiarity with short codes as trusted, official communication channels, understanding that messages from these numbers came from established businesses rather than potentially fraudulent sources.
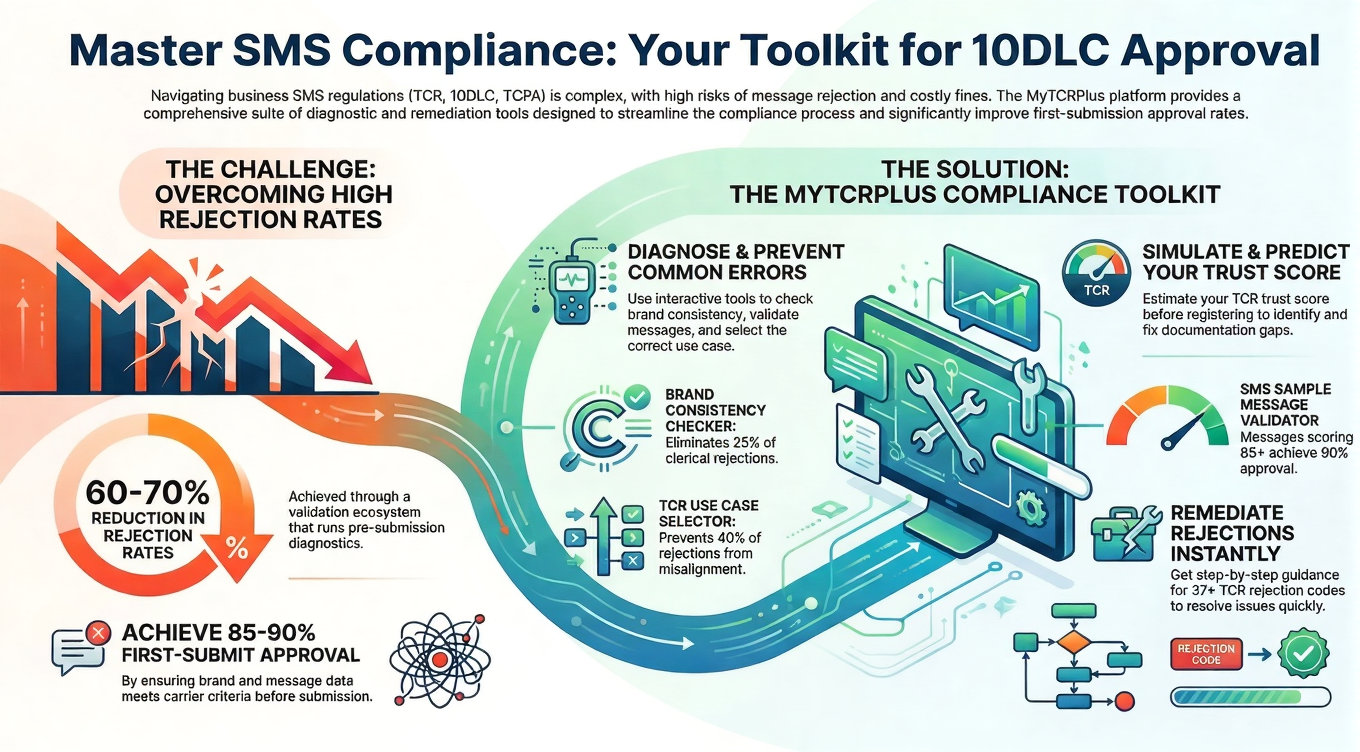
However, despite these advantages, short codes came with substantial barriers to entry that fundamentally limited who could participate in SMS marketing. The costs were prohibitive for smaller businesses and startups. Setup fees often reached thousands of dollars, with some carriers charging $500 to $1,500 just to establish a short code. Monthly maintenance expenses typically run $100 to $500 per month, and some codes in high-demand categories cost significantly more. For a small e-commerce operation running on tight margins, these costs could consume a substantial portion of the annual marketing budget before sending a single message.
Beyond the financial barriers, the approval process for short codes was notoriously lengthy and complex. Businesses had to work through carriers and aggregators, submitting detailed information about their messaging practices, use cases, and compliance procedures. The review process could take anywhere from two weeks to several months, during which a business might miss important marketing windows or promotional opportunities. Some businesses were rejected entirely, with little explanation and no clear path to appeal or remediation.
The carrier approval process also created a gatekeeping dynamic where short code availability was limited. Only certain numbers were available, and in high-demand areas, businesses might have to choose between paying premium rates for codes matching their brand identity or accepting whatever was available. This scarcity drove prices up and made planning uncertain.
The Evolution of Regulations and Carrier Strategies
The migration from short codes to 10DLC didn’t happen by accident or through sudden industry innovation. Rather, it resulted from deliberate decisions by major carriers responding to regulatory pressure, consumer complaints, and the growing epidemic of SMS spam and fraud that plagued the messaging ecosystem.
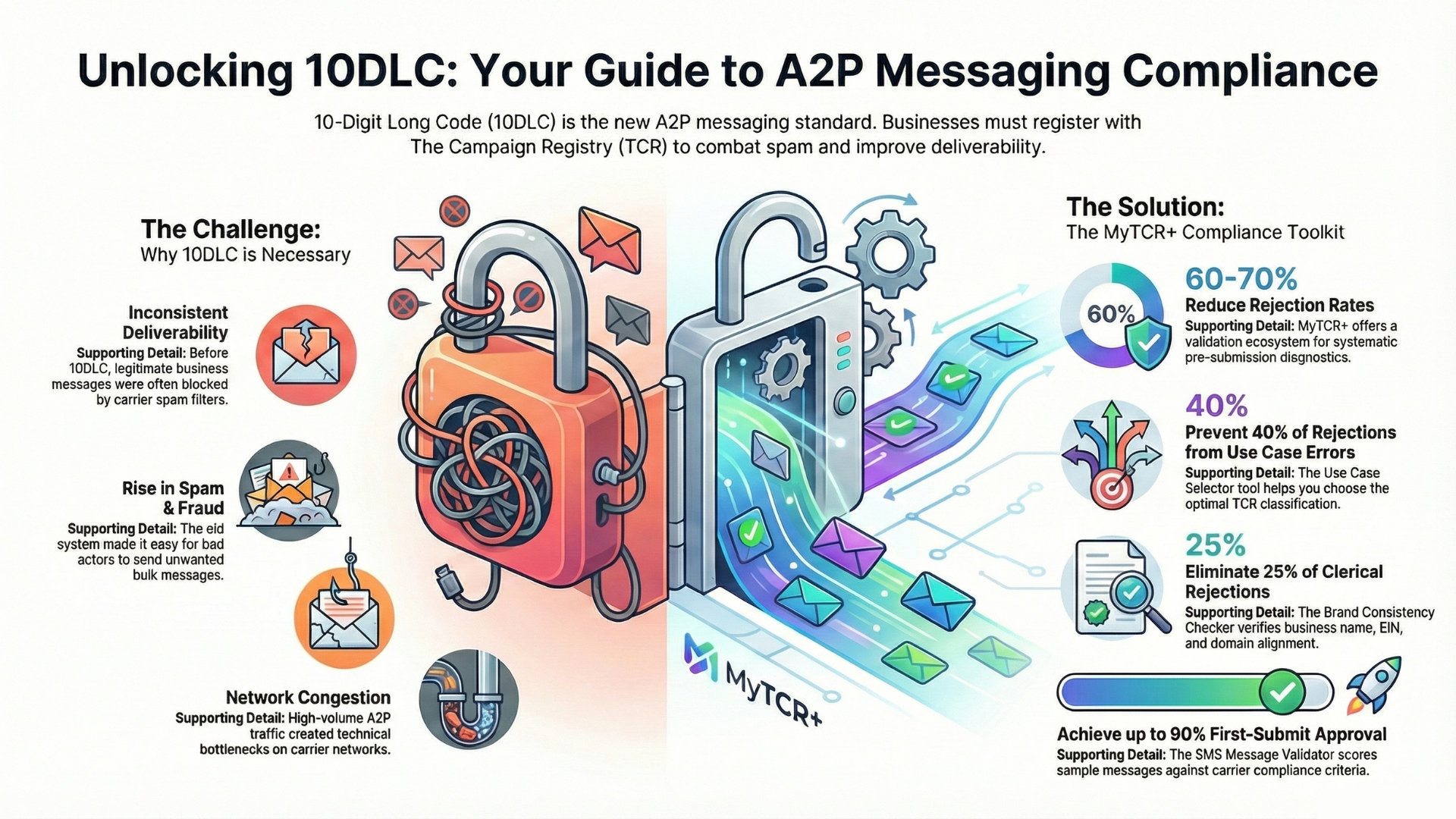
By the late 2010s, SMS spam had reached crisis proportions. Criminals and fraudsters had adapted to exploit the messaging channel, using combinations of spoofed numbers, compromised accounts, and malicious links to defraud consumers and breach security. Legitimate businesses found their messages competing for attention in inboxes increasingly filled with scams. Carriers faced regulatory scrutiny and complaints from consumers about their role in facilitating spam and fraud.
Recognizing the problem, major carriers began developing what would become 10DLC—a new framework designed to add trust, transparency, and accountability to business SMS communications. The goal was to create a system that would reduce spam and fraud while making legitimate business communications more trustworthy and deliverable. This shift represented a fundamental reconception of how carriers would handle business SMS going forward.
The 10DLC Revolution: Fundamentals and Framework
10DLC uses standard ten-digit phone numbers that appear identical to personal mobile numbers, resembling the familiar format consumers see when contacting friends, family, and businesses. This familiarity is intentional—it encourages consumers to trust the messages they receive, as they come from numbers that look like normal phone numbers rather than obviously commercial short codes.
The introduction of 10DLC by major carriers represents a paradigm shift in how business messaging infrastructure works. Unlike short codes, which were specifically designated for business use and carried identifiable commercial characteristics, 10DLC numbers look like regular cell phone numbers. This similarity to personal phone numbers makes them inherently more trustworthy to consumers while also making them more valuable for carriers to protect against abuse.
The technical framework behind 10DLC incorporates several key innovations. At its core is The Campaign Registry (TCR), a database maintained by TCPA-compliant aggregators and carriers that catalogs and verifies business messaging campaigns. When a business wants to send messages using 10DLC, they must register their specific campaigns with TCR, providing detailed information about their messaging practices, use cases, compliance procedures, and business details.
This registration system enables what carriers call “trust scoring” or “reputation scoring.” Each business messaging program receives a score based on factors including the nature of the business, the type of messaging being sent, the company’s compliance history, whether they’ve had previous regulatory violations, the percentage of recipients who mark messages as spam, and bounce rates or delivery failures. This scoring system directly influences throughput capabilities—a highly trusted business sending compliant messages might receive high message volume capabilities, while a new business or one with compliance concerns receives lower throughput until demonstrating reliability.
The Strategic Advantages of 10DLC for E-commerce
From the perspective of e-commerce platforms considering or undertaking the migration to 10DLC, the shift offers several substantial advantages despite the implementation challenges involved.
The most immediately obvious advantage is accessibility. Unlike short codes, which required expensive leasing arrangements and lengthy approval processes, 10DLC is available to businesses of all sizes at a fraction of the cost. The registration process through The Campaign Registry is significantly more streamlined. Instead of waiting months for carrier approval, businesses can often get registered and operational within days or weeks. The cost structure is also dramatically more favorable—businesses typically pay modest registration fees and per-message or subscription-based rates rather than high upfront and monthly costs.
This democratization of SMS marketing has profound implications for e-commerce platforms. Small to medium-sized retailers can now access professional SMS capabilities and compete with larger enterprises on messaging sophistication. A startup selling specialty products online can implement order confirmation messages, shipping notifications, and promotional campaigns using 10DLC without the prohibitive investment that short codes would have demanded. This leveling of the playing field has energized the e-commerce ecosystem.
A second major advantage is the alignment with modern consumer expectations and regulatory requirements. The 10DLC framework was specifically designed to combat spam and fraud while making legitimate business communications more trustworthy. This emphasis on transparency, consent, and compliance aligns well with how modern consumers expect to be treated. Consumers increasingly value their privacy and want to control their communication experiences with businesses. The 10DLC requirement for clear opt-in procedures, sender identification, and easy opt-out mechanisms respects these preferences.
Third, 10DLC provides better reputation management and control. Rather than relying on shared infrastructure where the behavior of other users can impact deliverability, businesses get individual reputation scores that reflect their specific practices. A business that maintains excellent compliance practices, honors opt-outs promptly, and sends relevant messages can build a strong reputation that ensures high deliverability. Conversely, poor practices immediately impact reputation and throughput, creating strong incentives for compliance.
For e-commerce platforms specifically, this reputation-based system creates an advantage for those operating at scale with diverse customer bases. A large retailer with millions of customers, strong compliance practices, and low spam complaint rates will receive high trust scores and excellent throughput. This means reliable message delivery precisely when it matters most—during critical business moments like flash sales or time-sensitive order notifications.
Fourth, 10DLC enables better compliance management and audit trails. The registration process requires businesses to document their messaging practices and use cases. This documentation creates a clear record of compliance intentions that can be referenced during audits or in disputes. The TCR maintains records of registered campaigns, creating accountability and making it easier for businesses to demonstrate compliance to regulators or in response to TCPA claims.
Navigating the Migration Process: Challenges and Considerations
Despite the significant advantages of 10DLC, the migration process from short codes requires careful planning and strategic execution. E-commerce platforms need to understand the challenges they’ll face and develop comprehensive strategies to address them.
The first major consideration is campaign registration and trust scoring. E-commerce platforms must register their campaigns with The Campaign Registry, providing detailed information about their messaging practices. For a large retailer with multiple distinct use cases—order confirmations, shipping notifications, promotional messages, customer service communications—this might mean registering multiple distinct campaigns, each with its own trust score and throughput allocation.
The registration process requires accuracy and completeness. Misrepresenting a use case, understating message volume, or providing inaccurate information can lead to registration denial, campaign suspension, or throttled throughput. E-commerce platforms should invest time in thoroughly understanding their messaging needs, categorizing their campaigns accurately, and providing comprehensive information during registration. Working with experienced compliance consultants or using platforms that automate TCR registration can help ensure accuracy.
A second significant consideration is throughput limitations relative to short code capabilities. While 10DLC throughput is generous for most business applications—typically allowing dozens or hundreds of messages per second—it may not match the astronomical volumes that short codes could handle. A massive retail operation sending millions of messages during a major flash sale event might find 10DLC throughput insufficient if they’ve underestimated their needs or not optimized their messaging strategy.
However, this limitation is often overstated. Most retailers can achieve their throughput needs through a combination of strategies: using multiple 10DLC numbers with distinct campaigns for different message types, optimizing messaging cadence and customer segmentation to spread volume over time, and working with carriers and aggregators to obtain higher throughput allocations based on demonstrated need and compliance. The key is realistic planning and understanding actual messaging needs rather than theoretical maximums.
A third major challenge is technical infrastructure updates. E-commerce platforms must update their messaging infrastructure to accommodate 10DLC requirements. This includes implementing proper opt-in procedures that capture explicit customer consent before sending promotional messages, ensuring clear identification of the sender in every message, and implementing robust opt-out mechanisms that process unsubscribe requests promptly and reliably. For platforms that previously relied on implicit consent or less formal opt-in procedures, this requires significant technical work.
Additionally, customer databases need to be reviewed and often cleaned to ensure compliance with carrier filtering requirements. 10DLC systems employ more sophisticated spam detection than previous frameworks, and carriers actively filter messages they believe are spam. Messages sent to recipients who didn’t explicitly opt in, messages with high complaint or bounce rates, and messages that don’t meet content guidelines are more likely to be filtered or rate-limited.
A fourth consideration is the transition period and potential service disruption. E-commerce platforms typically can’t simply abandon short codes overnight. The most practical approach involves running both systems in parallel during a transition period, gradually migrating customer communication preferences and traffic to 10DLC while maintaining short code operations for residual or exceptional use cases. This parallel operation requires careful planning to avoid customer confusion and ensure consistent messaging.
Best Practices for Successful Migration
Successful e-commerce platforms have developed best practices for managing the migration to 10DLC that minimize risk and maximize the benefits of the transition.
First, successful migrations begin with thorough planning and assessment. E-commerce platforms should audit their current messaging practices, identifying all distinct use cases, estimating volume requirements for each, and assessing compliance with current regulations. This assessment provides the foundation for realistic registration with TCR and planning infrastructure changes.
Second, successful platforms treat the migration as an opportunity to improve their overall messaging practices. Rather than simply replicating existing short code processes in 10DLC, they use the transition as a catalyst for implementing better consent management, improving message relevance and timing, enhancing customer preference controls, and strengthening compliance procedures. The result is not just a successful technical migration but also an improved customer communication experience.
Third, successful migrations involve clear communication with customers about the changes. E-commerce platforms should inform customers about the transition, explain what it means for their communication experience (generally, positive benefits like more reliable delivery and better sender identification), and clarify any changes to how customers can manage their communication preferences. Transparent communication builds trust and reduces customer confusion.
Fourth, successful migrations include comprehensive testing before full launch. E-commerce platforms should thoroughly test 10DLC message delivery, compliance procedures, customer preference controls, and opt-out mechanisms before relying entirely on the new system. Testing reveals technical issues before they impact customer communications and identifies training needs for staff managing customer inquiries.
Fifth, successful platforms maintain detailed records and documentation throughout the migration. They document their registration with TCR, maintain audit trails of customer consent, preserve records of messaging practices, and document compliance procedures. This documentation demonstrates regulatory compliance and provides evidence in case of disputes or audits.
The Long-Term Benefits and Future Positioning
Although the transition to 10DLC requires significant investment and planning, the long-term benefits justify the effort for most e-commerce platforms. The system’s emphasis on transparency, consent, and trust aligns with where customer expectations and regulatory frameworks are heading. E-commerce businesses that embrace this transition thoughtfully position themselves advantageously for the regulatory environment of the next decade.
The shift also reflects broader industry recognition that sustainable business messaging requires respecting customer preferences and maintaining trust. As SMS marketing matures and becomes more competitive, businesses that communicate responsibly and relevantly will maintain better customer relationships, achieve higher engagement rates, and face lower regulatory risk compared to those clinging to outdated practices.
Furthermore, as carriers and regulators continue refining their approach to business messaging, compliance leadership provides competitive advantage. Businesses that demonstrate strong compliance practices and maintain excellent reputation scores will find themselves with reliable, high-throughput messaging capabilities precisely when competitors with poor practices face throttling and filtering. This creates positive reinforcement for responsible practices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Evolution
The migration from short codes to 10DLC represents a significant evolution in how e-commerce platforms connect with customers through SMS. While the transition requires investment, planning, and technical updates, the benefits are substantial. Lower costs democratize SMS marketing, enabling smaller businesses to compete alongside larger enterprises. Better compliance frameworks reduce regulatory risk. Reputation-based trust scoring rewards responsible messaging practices. Alignment with consumer expectations around privacy and communication preferences strengthens customer relationships.
E-commerce businesses that approach this migration strategically—investing in proper registration, updating technical infrastructure thoughtfully, improving their overall messaging practices, and communicating clearly with customers—will find themselves better positioned to maintain strong, compliant, cost-effective customer relationships through reliable SMS messaging. The businesses that thrive will be those that view the migration not as a burden but as an opportunity to modernize their communication practices and demonstrate commitment to customer-centric, responsible messaging that serves both business objectives and customer preferences.