TCR Registration Deadline Enforcement: What February 2025 Blocking Means for Your Business
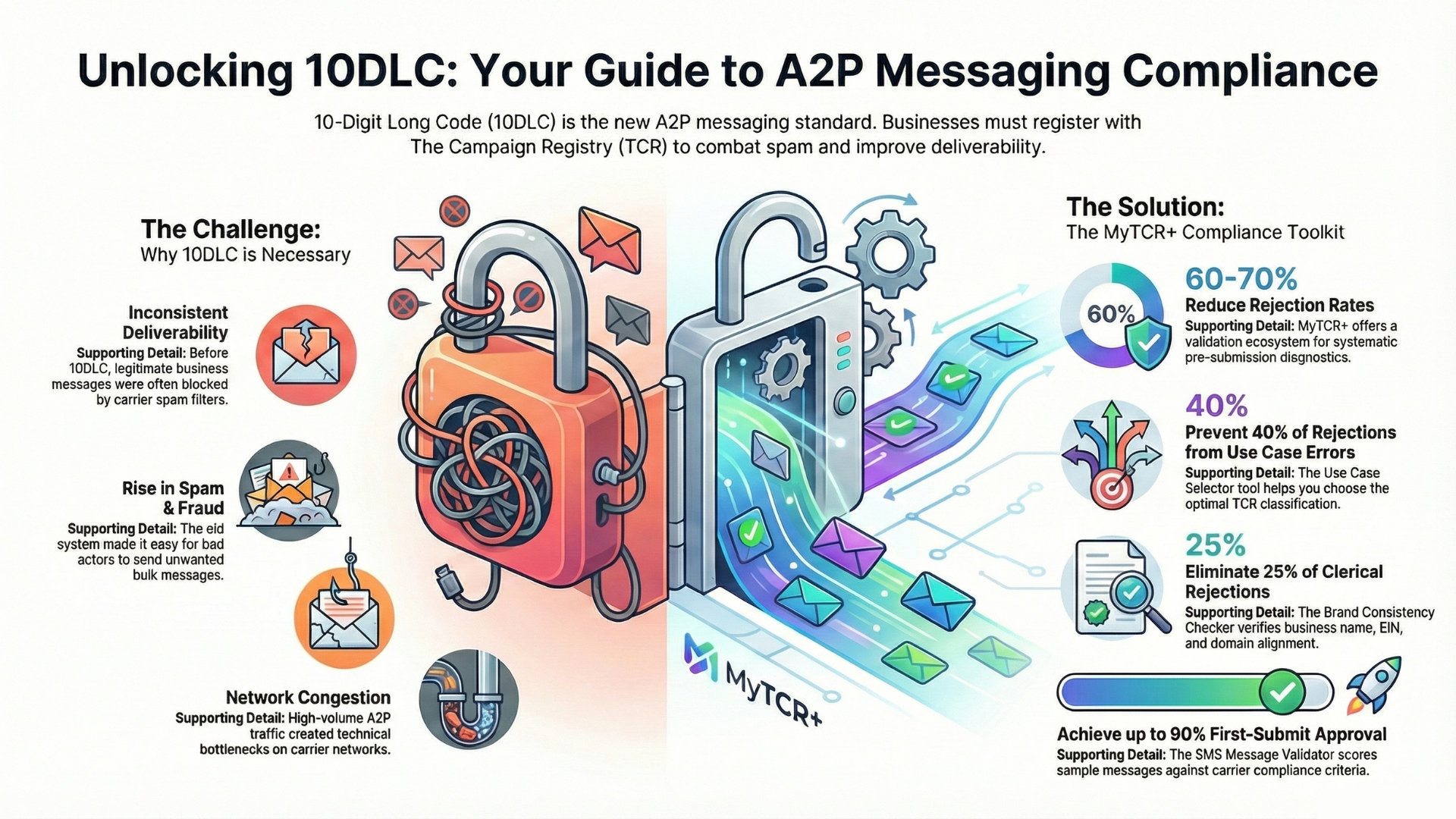
The messaging landscape shifts dramatically in February 2025 as carriers implement comprehensive blocking for unregistered business texting operations. This enforcement represents the final phase of The Campaign Registry (TCR) rollout, ending the grace period that allowed organizations to operate without proper 10DLC registration.
The transition from voluntary compliance to mandatory enforcement fundamentally alters business messaging operations. Companies that delayed registration now face immediate message blocking, carrier penalties, and potential legal exposure under TCPA regulations.
The End of Grace Period Operations
TCR enforcement eliminates the regulatory flexibility that characterized early 10DLC adoption. Carriers previously permitted limited unregistered messaging while organizations navigated registration requirements. February 2025 marks the termination of these accommodations.
Unregistered messaging traffic now triggers automatic blocking at the carrier level. These blocks operate independently of message content, sender reputation, or historical performance metrics. Registration status becomes the primary filter determining message deliverability.
The enforcement mechanism operates through carrier-level screening that validates TCR registration before message transmission. Messages from unregistered campaigns face immediate rejection, regardless of recipient consent or message urgency. This creates operational disruptions for organizations dependent on customer communications.
Carrier enforcement extends beyond simple blocking to include sender reputation penalties. Repeated attempts to send unregistered messages degrade sender scores, making future registration and message delivery more difficult. These reputation impacts persist beyond initial compliance efforts.
Immediate Operational Impacts
Message blocking creates cascading operational failures across customer-facing business processes. Appointment reminders, transaction confirmations, and support communications fail without warning or delivery receipts. Organizations experience communication blackouts that disrupt customer relationships and revenue generation.
Customer service operations face particular strain as traditional communication channels become unreliable. Support tickets increase as customers miss critical notifications, while staff lack visibility into message delivery failures. This creates operational overhead and customer satisfaction issues.
Sales processes dependent on SMS outreach experience immediate disruption. Lead nurturing sequences, follow-up communications, and conversion-critical messages fail to reach prospects. Organizations lose revenue opportunities while competitors with proper registration maintain competitive advantages.
Notification systems for time-sensitive communications fail unpredictably. Password resets, security alerts, and emergency notifications may not reach recipients, creating security vulnerabilities and operational risks. Organizations face potential liability for failed critical communications.
Financial and Legal Consequences
TCPA penalties for non-compliant messaging range from $500 to $1,500 per unauthorized message. Organizations sending substantial message volumes face catastrophic financial exposure under these regulations. Class action lawsuits targeting unregistered messaging operations create additional legal risks.
Carrier penalties compound financial impacts through sender reputation degradation and potential account suspension. Organizations may face messaging platform restrictions, rate limiting, or complete service termination. Restoring carrier relationships requires extensive remediation efforts and compliance investment.
Revenue disruption from failed customer communications creates measurable business impact. Organizations lose transaction completion rates, appointment attendance, and customer engagement metrics. These impacts extend beyond immediate message blocking to ongoing relationship degradation.
Compliance remediation costs include registration fees, legal consultation, and operational restructuring. Organizations must invest in consent management, message template compliance, and documentation systems. These costs multiply for organizations with multiple campaigns or complex messaging requirements.
Registration Components and Requirements
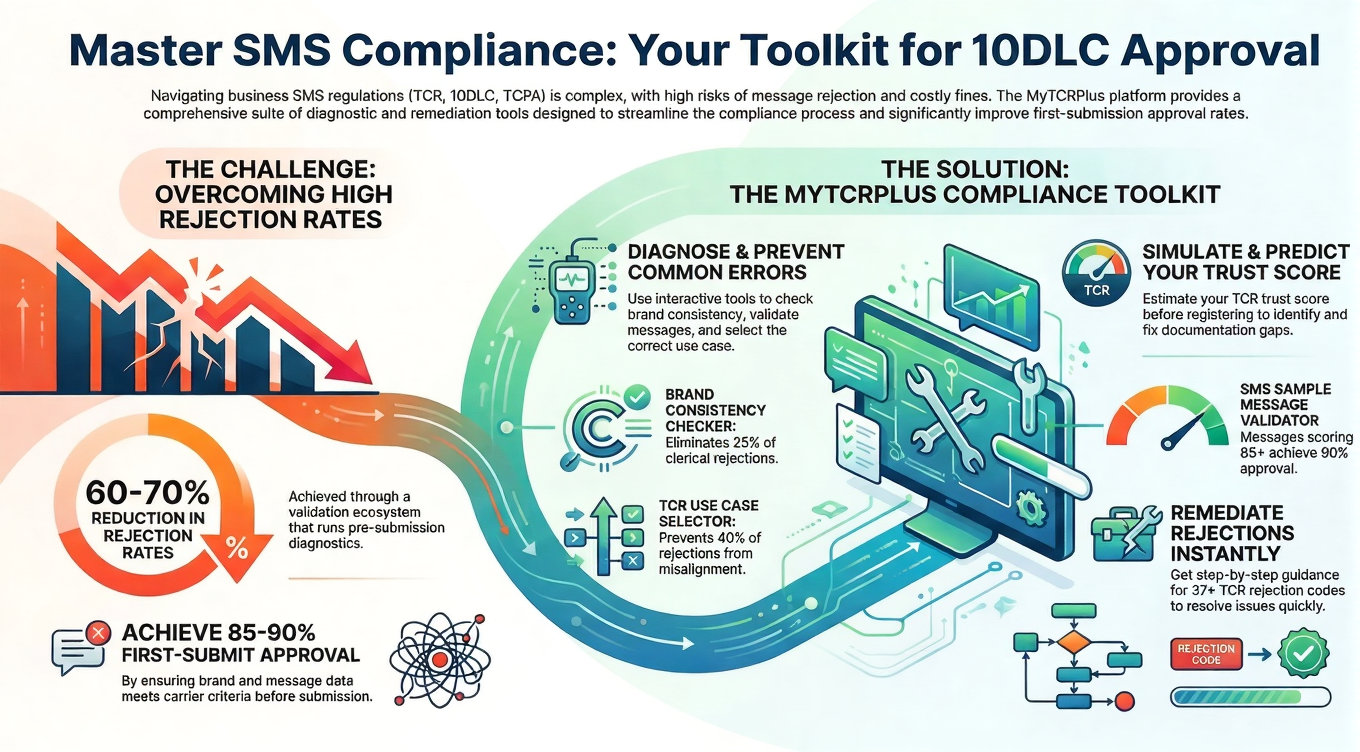
TCR registration requires comprehensive business verification including legal entity documentation, operational details, and use case specifications. Organizations must provide Employer Identification Numbers (EIN), business registration certificates, and detailed campaign descriptions.
Brand registration establishes organizational identity within the TCR system. This process validates business legitimacy, contact information, and website presence. Carriers use brand registration to assess sender credibility and approve messaging operations.
Campaign registration defines specific messaging use cases, consent mechanisms, and content categories. Organizations must document opt-in procedures, message frequency expectations, and compliance procedures. Campaign registration determines message filtering and throughput limits.
Sample message requirements demonstrate actual content organizations intend to transmit. These samples must include proper opt-out language, brand identification, and compliance disclosures. Carriers evaluate samples for content policy violations and TCPA compliance.
Consent and Documentation Standards
Proper consent collection requires explicit opt-in mechanisms that clearly communicate messaging expectations. Organizations must implement checkboxes that remain unchecked by default, provide detailed disclosure language, and document consent collection procedures.
Documentation requirements include consent records, opt-out processing, and audit trails. Organizations must maintain evidence of proper consent collection, including timestamps, IP addresses, and specific consent language used. This documentation supports compliance audits and legal defense.
Privacy policy requirements mandate specific language regarding SMS consent and data sharing practices. Organizations must clearly state that phone numbers and consent information will not be shared with third parties for marketing purposes. Privacy policies must be easily accessible from consent collection points.
Terms of service documentation must include messaging frequency disclosures, opt-out instructions, and support contact information. These disclosures must align with registered campaign use cases and provide clear expectations for message recipients.
Common Registration Failures and Remediation
Website compliance failures represent the most frequent registration rejection cause. Organizations must maintain functional websites with complete business information, accessible privacy policies, and proper contact details. Broken links or incomplete information trigger automatic rejections.
Consent language failures occur when opt-in forms lack required disclosures or use pre-checked consent boxes. Organizations must implement unchecked opt-in mechanisms with complete disclosure language including opt-out instructions and frequency expectations.
Sample message non-compliance includes missing brand names, inadequate opt-out language, or content misalignment with declared use cases. Organizations must ensure all sample messages include proper branding and compliance elements while accurately representing intended messaging content.
Business entity verification failures affect sole proprietorships and unincorporated businesses. TCR requires formal business registration as LLC or corporation structures. Organizations operating as sole proprietorships must restructure or face automatic rejection.
Industry-Specific Compliance Challenges
Healthcare organizations face complex consent requirements under HIPAA and state privacy regulations. Messaging must comply with healthcare privacy standards while meeting TCR registration requirements. This creates documentation burdens and operational complexity.
Financial services encounter additional compliance layers under federal banking regulations and state financial privacy laws. Messaging content must avoid prohibited financial advice while maintaining TCR compliance standards. Registration processes require enhanced documentation and approval procedures.
Educational institutions must navigate FERPA requirements alongside TCR compliance. Student communication systems require enhanced privacy protections while maintaining operational efficiency. This creates technical and procedural complexity for institutional messaging.
E-commerce operations face particular challenges with transactional messaging classification. Cart abandonment messages, shipping notifications, and promotional content require separate campaign registrations with distinct consent mechanisms.
Carrier Relationship Management
Carrier approval processes evaluate registration completeness, compliance history, and operational readiness. Organizations with incomplete registrations face delayed approval cycles and potential additional documentation requests. Proper preparation accelerates approval processes.
Sender reputation management becomes critical for long-term messaging success. Organizations must maintain positive sending practices, process opt-outs promptly, and avoid content policy violations. Reputation degradation affects message deliverability and carrier relationships.
Message filtering and throughput limits vary based on campaign registration and sender reputation. Organizations may experience rate limiting or content filtering based on registration completeness and compliance history. Understanding these limitations prevents operational disruptions.
Carrier policy evolution requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Messaging standards continue evolving, requiring organizations to maintain current compliance practices and documentation. Proactive policy monitoring prevents future compliance failures.
Remediation Strategies and Timeline
Immediate remediation requires comprehensive registration audit and gap analysis. Organizations must assess current compliance status, identify missing documentation, and prioritize critical registration components. This assessment guides remediation planning and resource allocation.
Registration acceleration strategies include professional compliance consultation and expedited processing services. Organizations can engage specialized providers to streamline registration processes and ensure complete submission. This reduces time-to-compliance and operational risk.
Interim messaging solutions may include alternative communication channels while registration processes complete. Organizations can implement email campaigns, website notifications, or alternative messaging platforms to maintain customer communications during compliance transitions.
Long-term compliance maintenance requires ongoing monitoring, documentation updates, and policy adherence. Organizations must establish compliance management processes that accommodate regulatory changes and operational evolution.
Future Regulatory Evolution
Carrier policy enforcement continues evolving toward stricter compliance standards and enhanced verification requirements. Organizations should expect additional documentation requirements, enhanced consent validation, and expanded audit procedures.
Industry consolidation among messaging providers creates concentration risk for compliance management. Organizations must evaluate provider compliance capabilities and disaster recovery options to maintain operational continuity.
Cross-channel compliance requirements may expand to include email marketing, push notifications, and other digital communication channels. Organizations should prepare for integrated compliance management across communication platforms.
Regulatory penalties face potential increases under evolving TCPA enforcement and state privacy regulations. Organizations must prepare for enhanced penalty structures and expanded regulatory oversight.
The February 2025 enforcement deadline represents a fundamental shift from voluntary compliance to mandatory operational requirement. Organizations that delay registration face immediate operational disruption, financial penalties, and competitive disadvantage. Proper registration requires comprehensive preparation, documentation, and ongoing compliance management.
Successful organizations approach TCR compliance as operational infrastructure rather than regulatory burden. This perspective enables strategic planning, resource allocation, and competitive positioning in the evolving messaging landscape. Compliance becomes a business enabler rather than operational constraint.
The messaging industry transformation continues beyond February 2025 as carriers implement enhanced verification requirements and expanded compliance standards. Organizations that establish robust compliance foundations position themselves for long-term success in regulated messaging environments.
RELATED POSTS
You may also like
SMS Compliance: Where to Start Your…
In today’s digital-first business environment, messaging platforms have become essential tools for…
10DLC Basics: Application-to-Person Messaging Explained
In today’s digital landscape, businesses rely heavily on text messaging to connect…
10DLC Basics: A2P Messaging Explained for…
If you’re planning to send marketing text messages to customers in the…
Streamlined Compliance, Zero Rejections
- Carrier-Friendly Structure—Designed for TCR/10DLC approvals
- Required Disclosures Included—Privacy, Terms, opt-in/opt-out language
- Sample Messages—Clear examples for provider review
- Hands-Off Hosting—Updates, SSL, and support included